共计 3895 个字符,预计需要花费 10 分钟才能阅读完成。
使用 CRA 创建支持 TS 的项目
React 脚手架工具 create-react-app(简称:CRA)默认支持 TypeScript
创建支持 TS 的项目命令:npx create-react-app 项目名称 --template typescript
当看到以下提示时,表示支持 TS 的项目创建成功: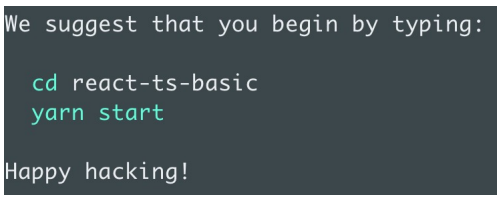
更多:在已有项目中使用 TS
相当于非 TS 项目
目录结构主要以下三个变化:
- 项目根目录中增加了
tsconfig.json配置文件:指定 TS 的编译选项(比如,编译时是否移除注释) - React 组件的文件扩展名变为:
*.tsx - src 目录中增加了 react-app-env.d.ts React 项目中默认的类型声明文件
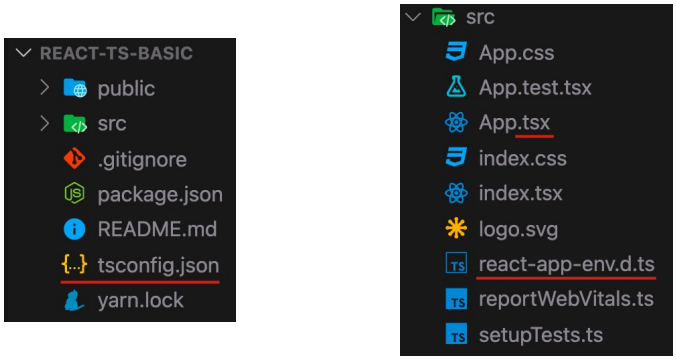
React 项目默认的类型声明文件 react-app-env.d.ts
三斜线指令:指定依赖的其他类型声明文件,types 表示依赖的类型声明文件包的名称
告诉 TS 帮我加载 react-scripts 这个包提供的类型声明
react-scripts 的类型声明文件包含了两部分类型:
- react、react-dom、node 的类型
- 图片、样式等模块的类型,以允许在代码中导入图片、SVG 等文件
TS 会自动加载该 .d.ts 文件,已提供类型声明(通过修改 tsconfig.json 中的 include 配置来验证)
TS 配置文件 tscongif.json
tsconfig.json 指定:项目文件和项目编译所需的配置项
TS 的配置项非常多(100+),以 CRA 项目中的配置为例来学习,其他的配置项用到时查文档即可
- tsconfig.json 文件所在目录为项目根目录(与 package.json 同级)
- tsconfig.json 可以自动生成,命令:
tsc --init
除了在 tsconfig.json 文件中使用编译配置外,还可以通过命令行来使用
使用演示:tsc hello.ts --target es6
- tsc 后带有输入文件时(比如,
tsc hello.ts),将忽略 tsconfig.json 文件 - tsc 后不带输入文件时(比如,
tsc),才会启用 tscconfig.json
推荐使用 tsconfig.json 配置文件
React 中的常用类型
前提声明:基于 class 组件 React+TS 的使用(不是 ReactHooks)
在不使用 TS 时,可以使用 prop-types 库,为 React 组件提供类型检查
TS 项目中,推荐使用 TypeScript 实现组件类型校验(代替 PropTypes)
不管是 React 还是 Vue,只要是支持 TS 的库,都提供了很多类型,来满足该库对类型的需求
- React 项目是通过
@types/react、@types/react-dom类型声明包,来提供类型的 - 这些包 CRA 已帮我们安装好(react-app-env.d.ts),直接用即可
函数组件的类型
- 组件的类型
- 组件的属性(props)
- 组件属性的默认值(defaultProps)
- 事件绑定和事件对象
函数组件的类型以及组件的属性

实际上,还可以直接简化为(完全按照函数在 TS 中的写法):
import { FC } from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type Props = { name: string; age?: number }
/* const Hello: FC<Props> = ({ name, age }) => (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
</div>
) */
// 完全利用 JS(TS)自身的能力来编写组件
const Hello = ({ name, age }: Props) => (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
</div>
)
const App = () => (
<div>
<Hello name="Joe" age={18}></Hello>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))函数组件属性的默认值(defaultProps)
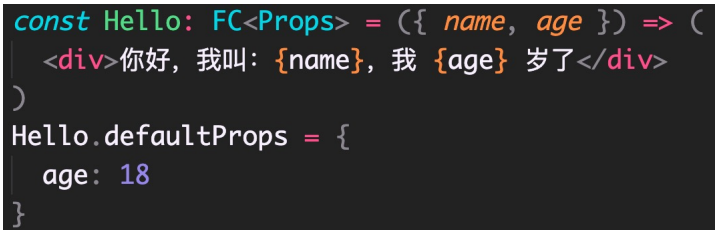
实际上,还可以直接简化为(完全按照函数在 TS 中的写法):
import { FC } from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type Props = { name: string; age?: number }
/* const Hello: FC<Props> = ({ name, age }) => (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
</div>
)
Hello.defaultProps = {
age: 18
} */
// 完全利用 JS(TS)自身的能力来编写组件
const Hello = ({ name, age = 18 }: Props) => (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
</div>
)
const App = () => (
<div>
<Hello name="Joe"></Hello>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))事件绑定和事件对象
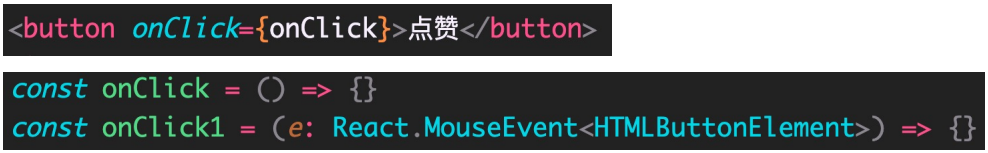
再比如,文本框: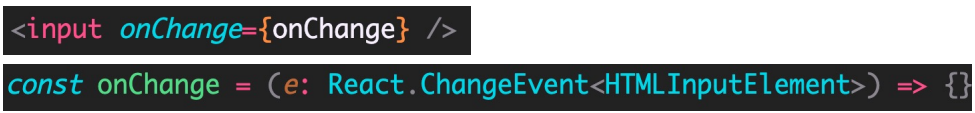
技巧:在JSX 中写事件处理程序(
e => {}),然后,把鼠标放在 e 上,利用 TS 的类型推论来查看事件对象类型
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type Props = { name: string; age?: number }
const Hello = ({ name, age = 18 }: Props) => {
const onClick = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
console.log('赞', e.currentTarget)
}
const onChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
console.log(e.target.value)
}
return (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
<button onClick={onClick}>点赞</button>
<input type="text" onChange={onChange} />
</div>
)
}
const App = () => (
<div>
<Hello name="Joe"></Hello>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))class 类组件的类型
- 组件的类型、属性、事件
- 组件状态(state)
class 组件的类型

import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type State = { count: number }
type Props = { message?: string }
class C1 extends React.Component {} // 无 props 无 state
class C2 extends React.Component<Props> {} // 有 props 无 state
class C3 extends React.Component<{}, State> {} // 无 props 有 state
class C4 extends React.Component<Props, State> {} // 有 props 有 state
const App = () => <div></div>
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))class 组件的属性和属性默认值
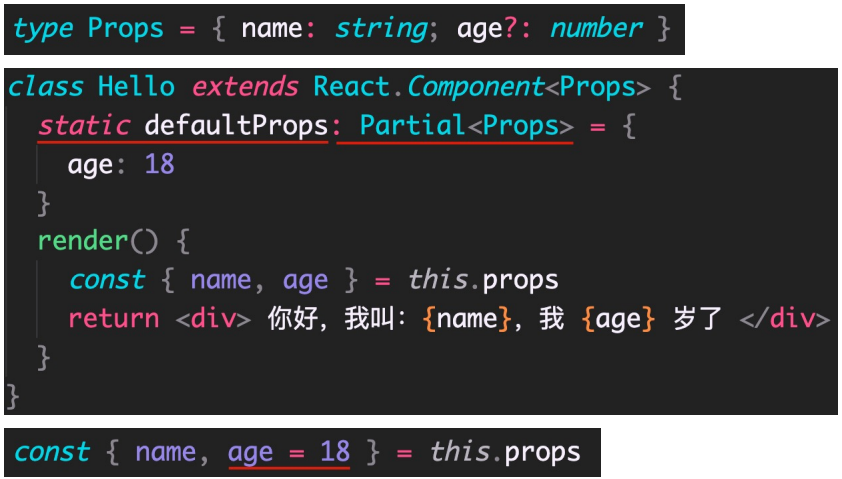
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type Props = { name: string; age?: number }
class Hello extends React.Component<Props> {
// 默认值
/* static defaultProps: Partial<Props> = {
age: 18
} */
render() {
// 简化 class 组件的属性默认值
const { name, age = 18 } = this.props
return (
<div>
你好,我叫:{name},我 {age} 岁了
</div>
)
}
}
const App = () => (
<div>
<Hello name="Joe"></Hello>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))class 组件状态(state)和事件
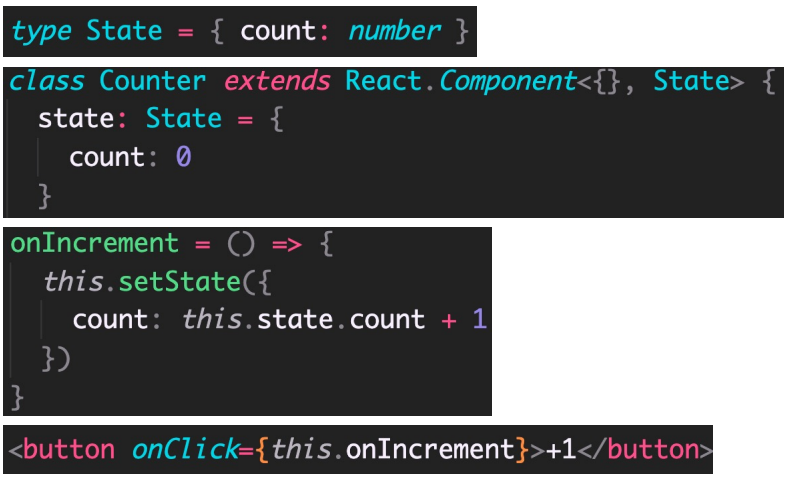
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
type State = { count: number }
class Counter extends React.Component<{}, State> {
state: State = {
count: 0
}
onIncrement = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>count: {this.state.count}</h3>
<button onClick={this.onIncrement}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
const App = () => (
<div>
<Counter></Counter>
</div>
)
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))